
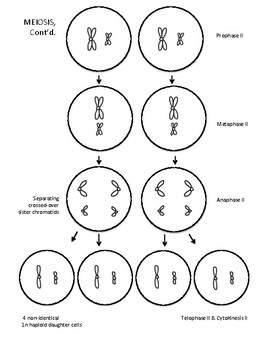
Now that the chromosomes are separated, two new cells are formed. During anaphase the chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle and move to opposite sides of the cell.ĥ. Each chromosome attaches itself to a spindle fiber.Ĥ. During this stage of mitosis, the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell along the equator.


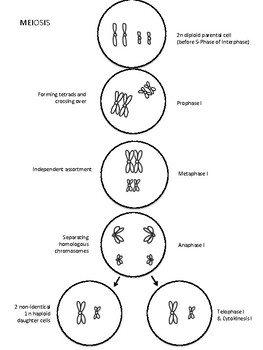
Color all of the chromatids and chromosomes blue.ģ. In all of the rest of the cell phases, these will be the same color.Ĭhromosomes are in the shape of an X where one half is the original chromosome and the other half is the copy. Color the aster pink and the spindle green. The centrioles form a star shaped structure called the aster and a spindle forms between them. The nuclear membrane breaks apart and the chromatin condenses into chromosomes. Color the centrioles red and the nuclear membrane yellow. At this time the cell grows, the DNA replicates, and organelles grow in preparation for cell division. A pair of centrioles are present (but inactive in the cytoplasm) and the nucleolus is visible. During this phase, the DNA is uncoiled and is called chromatin. A cell spends most of its time in this "in between" phase performing cell activities like cellular respiration, osmosis, and for plant cells, photosynthesis. A phase called interphase is not actually part of mitosis, but is the resting phase that the cell is in when it is not dividing.ġ. The cell cycle has five phases, but mitosis (nuclear) division occurs in four steps: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase. HS-LS1-4 Use a model to illustrate the role of cellular division (mitosis) and differentiation in producing and maintaining complex organisms.Cell division includes a very important process called MITOSIS where the nucleus creates a copy of all of its DNA so that each new cell is an exact copy of the parent cell and contains the exact same number of chromosomes. Grade Level: 8-9 | Time Required: 30-40 minutes This worksheet can be used as reinforcement for a lesson on mitosis and the cell cycle. Students must also label cell structures like the centrioles, aster, spindle, and nuclear membrane. Students read about each of the phases of the cell cycle and label and color a diagram that shows details of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
